Why Folate Matters to the Brain
Folate (vitamin B9) is fundamental to normal brain development and function.
It supports multiple biological processes essential for neurological health, including:
DNA synthesis and cell division

Neurotransmitter production

Myelination of nerve fibers

Methylation reactions involved in gene regulation
The developing brain requires higher concentrations of folate than the rest of the body,
emphasizing the importance of efficient folate transport into the central nervous system.
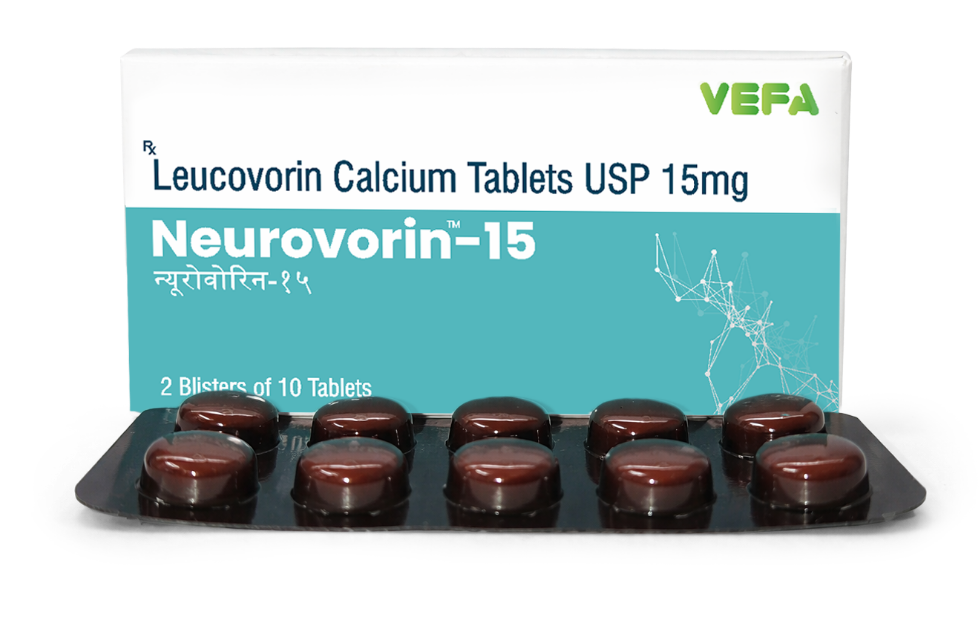
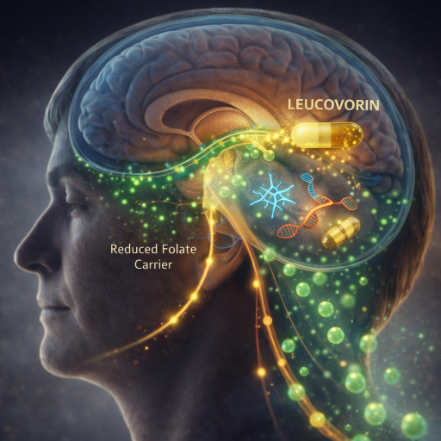
What Is Leucovorin?
Leucovorin, also known as folinic acid, is a biologically active, reduced form of folate.
Unlike folic acid (a synthetic precursor), leucovorin:
Enters the folate cycle directly
Does not require enzymatic activation

Has been used clinically for decades in oncology and hematology
Its established pharmacology and safety profile make it a subject of interest in conditions
involving impaired folate metabolism or transport.
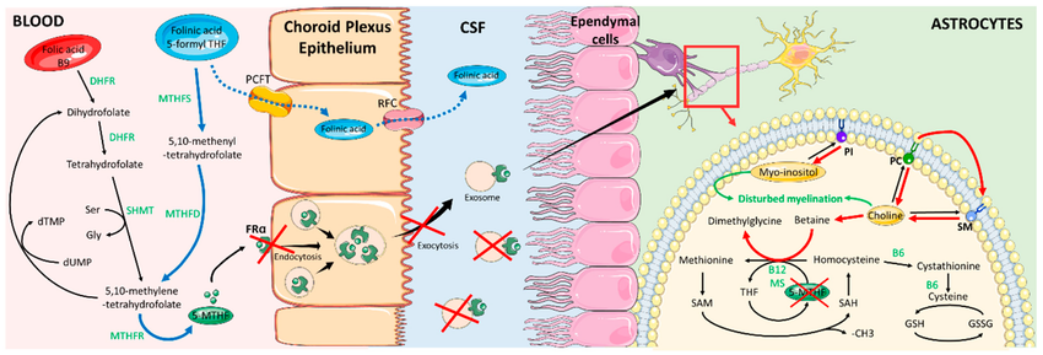
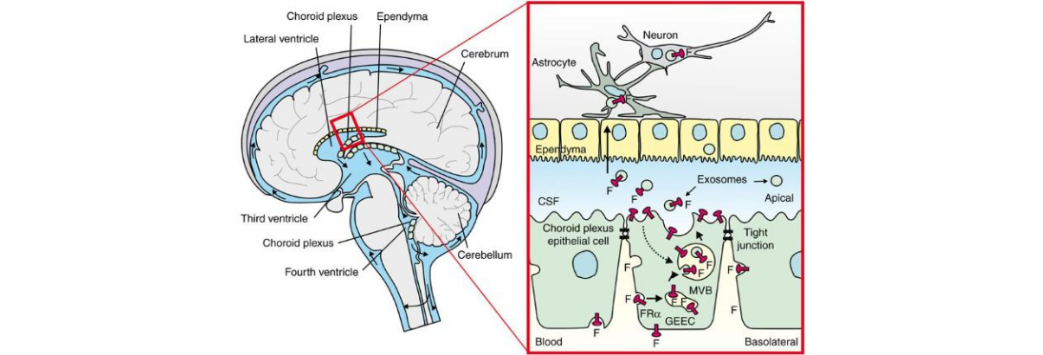
Cerebral Folate Deficiency (CFD): A Key Concept
Cerebral folate deficiency is a neurological condition where folate levels in the
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) are reduced, despite normal blood folate levels.
Why does this happen?
In many individuals, folate entry into the brain is impaired due to:
- Dysfunction of the folate receptor alpha (FRα) at the choroid plexus
- Presence of folate receptor alpha autoantibodies (FRAA) that block or terfere with folate transport
CFD has been associated with:
- Developmental delay
- Epilepsy and movement disorders
- Neurodevelopmental regression
- Autism-like features

Connection Between CFD and Autism Spectrum Disorder
Research over the last decade has shown that a biologically distinct subgroup of children
with ASD may exhibit features of cerebral folate deficiency
Published studies report:
Reduced CSF folate levels in subsets of children with ASD
High prevalence of folate receptor alpha autoantibodies
Increased folate requirements due to metabolic and mitochondrial factors
Meta-analyses suggest that approximately 58-76% of children with ASD may demonstrate
biochemical features consistent with CFD.
How Leucovorin Is Scientifically Rationale in This Context
When the primary folate transport pathway (via folate receptor alpha) is
impaired, leucovorin may help by:
- Utilizing alternative transport mechanisms, such as the reduced folate
carrier - Increasing intracellular folate availability in the brain
- Supporting key processes including neuronal metabolism, myelination,
and methylation
This mechanistic rationale has driven clinical research into leucovorin for
conditions associated with cerebral folate deficiency.
Clinical Research Snapshot: Autism

A double-blind, placebo-controlled trial in children with ASD and language impairment demonstrated:
- Significant improvement in verbal communication over 12 weeks
- Greatest benefit observed in children positive for folate receptor autoantibodies
- Safety profile comparable to placebo

Additional controlled studies and systematic reviews across multiple regions have reported:
- Improvements in communication and adaptive behavior
- Reductions in autism symptom severity scores
- Consistent benefit in biologically defined subgroups, rather than across all individuals with ASD
Beyond Autism: Other Neurodevelopmental Conditions
Leucovorin is an accepted therapy in confirmed cases of cerebral folate deficiency, where it has been associated with improvements in neurological outcomes.
CFD has also been reported in:
- Epilepsy and movement disorders
- PANS/PANDAS
- Neuropsychiatric and neurodegenerative conditions
Safety Overview (From Published Studies)
Across clinical trials in neurodevelopmental disorders:

Typical research doses ranged from ~0.5–2 mg/kg/day, maximum 50mg/day

Leucovorin was generally well tolerated

Most reported adverse effects were mild and transient
Disclaimer: Leucovorin (folinic acid) is not approved for the treatment of autism spectrum disorder (ASD) or other neurodevelopmental disorders.
This page is intended as a scientific information resource based on published clinical research.
Any off-label use must be determined by a qualified healthcare professional based on individual patient assessment.